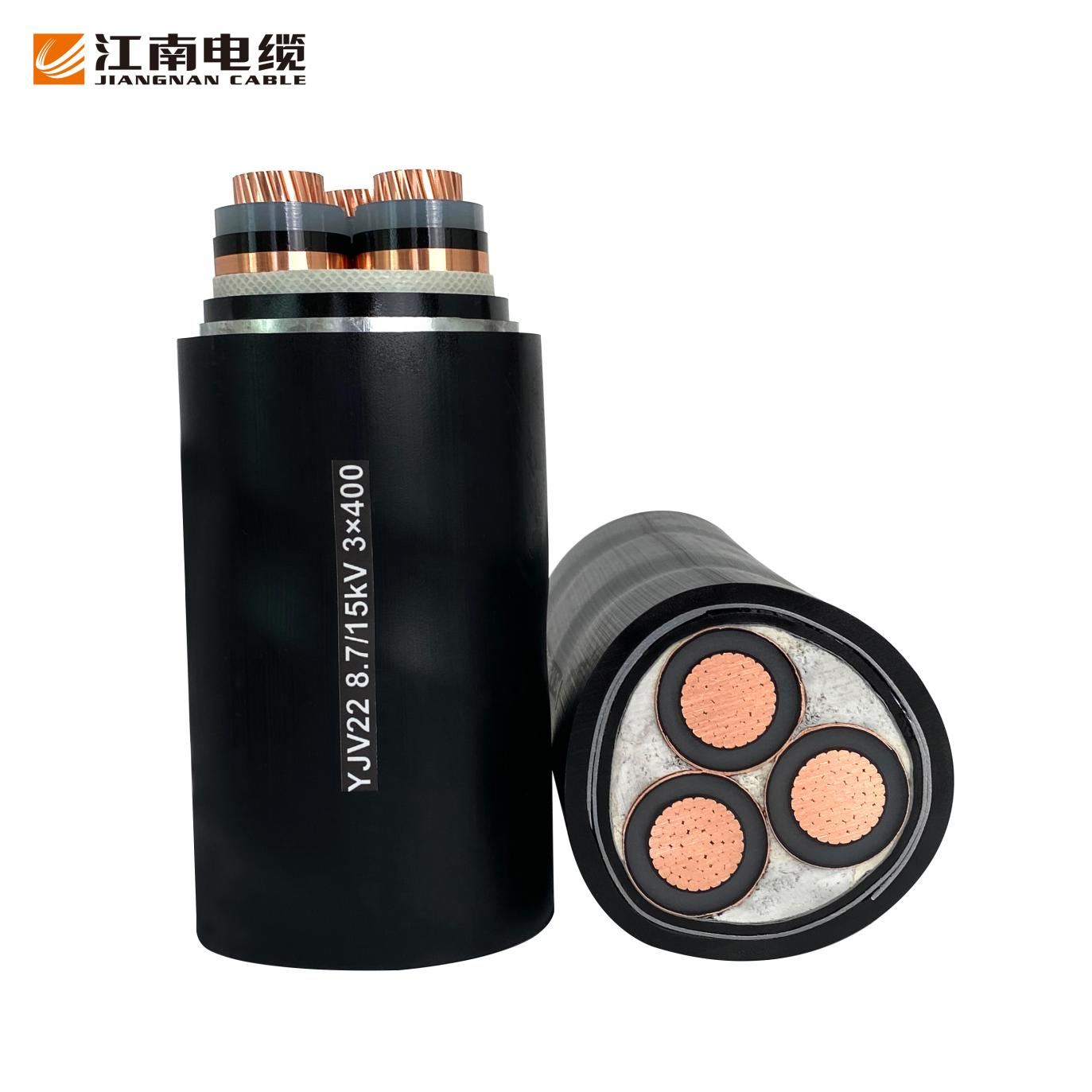
Ultimate Guide to Underground Power Cables: Types, Standards, and Protection
Why Underground Power Cables Are Different
Most people see power lines strung on poles and forget that a huge part of electricity runs quietly underground. Underground power cables aren't just "buried wires." They face soil pressure, water seepage, chemical exposure, and the risk of damage from nearby construction. That's why their design, installation, and maintenance are more demanding than overhead lines.
Types of Underground Power Cables
Underground cables are categorized by the voltage they carry.
- Low Voltage (LV) – Usually, these provide street lighting, small businesses, and residences. They are mostly installed in residential areas and function below 1 kV.
- Medium Voltage (MV) – These cables, which range in voltage from 1 kV to 33 kV, serve regional distribution networks, business complexes, and industrial estates.
- High Voltage (HV) – Cross-country transmission, substations, and power plants employ voltages higher than 33 kV. Stricter requirements, stronger shielding, and thicker insulation are needed for them.
Think of it like plumbing: a garden hose (LV), a city water main (MV), and a dam pipeline (HV). Each has different pressure and design needs.
Installation Standards for Underground Power Cables
Standards matter because a poorly installed underground cable can fail long before its rated lifespan. Three factors stand out:
Trench Depth and Backfill Requirements
Cables must be buried far enough to prevent unintentional damage from frost, digging, and vehicles, etc. In many countries, LV cables are laid at 600 mm depth, while HV may go as deep as 1.2 meters. Backfilling with fine sand or screened soil is essential to protect the insulation.
Minimum Bend Radius
A cable is not a rope—it cannot just bend sharply. Manufacturers specify a minimum bend radius (often 12–15 times the cable diameter). Exceeding this can damage insulation and shorten life. Installers sometimes use wooden rollers to avoid “kinking” the cable during laying.
Clearance
Proper spacing should be provided between the cables, water pipes, and gas lines. By doing these steps, harmful interactions are avoided and heat dissipation is guaranteed. For example, according to certain norms, there should be 300 mm between you and other utilities.
Protection Methods for Underground Power Cables
Underground cables face constant issues. To prolong their lives, engineers use a variety of techniques like:
1. Water intrusion is prevented by moisture barriers, which are made of metal or plastic sheaths. Even very small amounts of moisture can cause conductors to degrade or partially discharge.
2. Cables with steel wire armor are protected from a variety of issues, including mechanical stress, rodents, and accidental digging.
3. Chemical-resistant jackets protect cables from acids, oils, and other corrosive substances when cables are in areas with contaminated soil or industrial waste.
In order to warn potential diggers before they reach the line, some projects even place warning tapes above the cable trench.
![Ultimate Guide to Underground Power Cables: Types, Standards, and Protection 1]()
Common Issues with Underground Cables
Despite careful planning, problems still arise. The most common include:
- Insulation Aging – Heat cycles, moisture, and stress cause cracks or brittleness over decades.
- Water Treeing – Microscopic moisture pathways slowly degrade insulation, which can lead to a major cause of medium-voltage failures.
- Mechanical Damage – Construction machinery or even rodents can damage the cable sheaths.
- Overheating – Poor soil thermal conductivity or overloaded circuits that trap heat can reduce the lifespan of cables.
Maintenance and Inspection Tips
Underground cables are hidden and we can't see them directly. But some preventive steps can help:
- Thermal Imaging – Identifies hotspots before breakdown occurs.
- Sheath Testing – Detects weak points in insulation.
- Soil Checks – Verify that there is no waterlogging or chemical contamination close to cable paths.
- Periodic Load Review – Prevents cables from carrying more current than they were designed for.
How to Choose the Right Underground Cable Supplier
- Adhere to IEC and national requirements.
- Test certificates for fire performance, bending resistance, and insulating resistance should be provided.
- Provide robust after-sales assistance, particularly for large installations.
- Provide tailored designs for industrial zones, difficult soil, and marine environments.
Paying a little more up front is preferable to having to deal with expensive downtime brought on by cable breakdowns.
Conclusion and Call to Action
Underground power cables are the most important part of modern energy networks. Their design, installation, and protection require much more attention than stringing wires overhead. From trench depth to moisture barriers, every factor counts toward longevity.
If you are planning a project, whether it is a housing scheme or a utility upgrade, then you must choose cables and suppliers who meet proper standards. The cost of prevention is far lower than the expense of replacing failed underground lines.