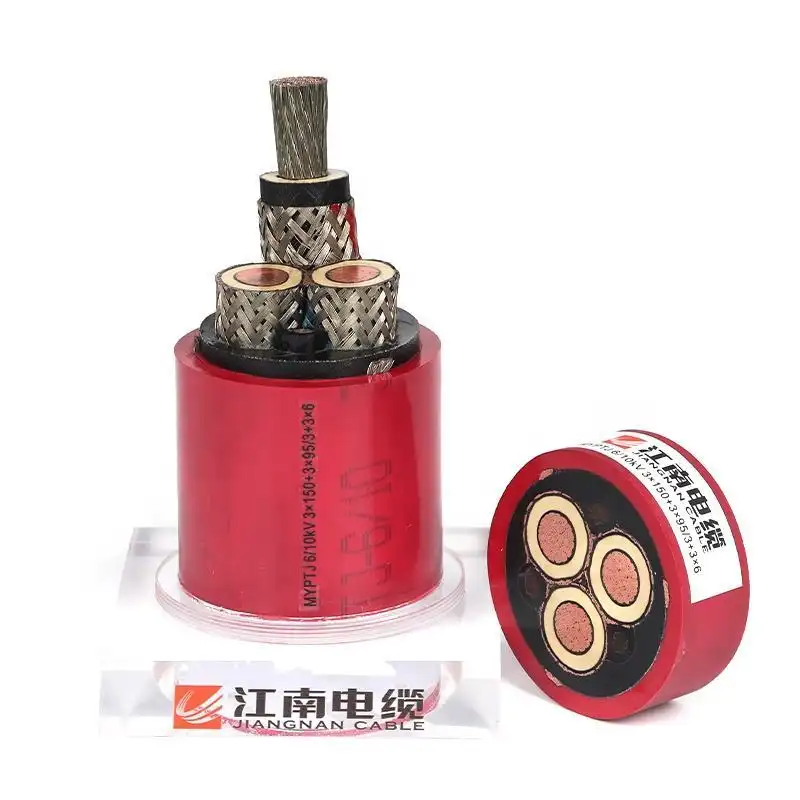
Mineral Insulated Cable
● The rated voltage of mineral-insulated cables:light load(BTTQ、BTTVQ、WD-BTTYQ)500V and heavy load (BTYTZ、BTTVZ 、WD-BTTYZ)750V.
● Testing voltage of mineral-insulated cables:light load 2000V/1min and heavy 2500V/1min.
● The insulation resistance of mineral-insulation cables shall be more than 1000MW; when the length of cable is less than 1000m, the insolation resistance shall be more than 10,000MW.
● Long-term service temperature of mineral-insulated cables:The long-term service temperature of mineral insulated cables is 70℃.In areas inaccessible to people ,the long-term service temperature is 105℃;in special high temperature circumstance,the long-term service temperature can reach 250℃.When the temperature keeps at 950-1000℃, the cable can sustain power supply for at least 3 hours;during a short or extremely short period,the service temperature can reach 1083℃.
● Curve radius:The possible minimum curve radius of mineral-insulated cables shall be in line with the above form.
| Manufacturing standard of MI cable | GB/T13033-2007 mineral insulated cable with a rated voltage not exceeding 750V and its terminals |
| IEC60702-2002 mineral insulated cable with a rated voltage not exceeding 750V and its terminals | |
| BS6207-2001 mineral insulated cable with a rated voltage not exceeding 750V | |
| Performance standard of MI cable | BS6387 performance requirements for cable required to maintain circuit integrity under fire conditions Britain |
| GA306.1~306.2-2007 Fire standard of Ministry of Public Security | |
| IEC60332-3 Test during flame combustion of cable | |
| GB/T18380.1-.3-2001 Test during flame combustion of cable | |
| GB/T17651.2-1998 Smoke density test of the cable under specific combustion | |
| GB/T17650.2-1998 Test on gases evolved during combustion of cable | |
| GB/T19216-2003 Test method of fire resistant characteristics on cable | |
| IEC60331 Cable fire resistance characteristics | |
| UL2196 Test of fire resistant cables USA | |
| IEC60754-2 Test of extracted gases from burning of cable materials | |
| IEC60134-2 Smoke density test | |
| Application standard of MI cable | GB50016-2014 Code for fire protection design of buildings |
| JGJ16-2008 Code for electrical design of civil buildings | |
| GB50217-2007 Code for design of power engineering cables | |
| GB50116-2013 Code for design of automatic fire alarm system | |
| GB50157-2013 Code for metro design | |
| GB50067-97 Code for fire protection design of garage,motor repair shop and parking area | |
| GB50333-2002 Technical code for buildings of hospital and clean operating department | |
| DBJ50-054-2006 Code for the fire protection design of big commercial buildings(Chongqing) | |
| DGJ08-2048-2008 Code for the fire protection design of wires and cables of civil buildings(Shanghai) | |
| DB21/T2116-2013 Technical regulation for fire protection safety of buildings(Liaoning) | |
| DBJ50-164-2013 Code for the fire protection design of wires and cables of civil buildings(Chongqing) | |
| 09D101-6 Laying of mineral insulated cables | |
| JGJ232-2011Technical regulation for the laying of mineral insulated cables | |
| BS5345 Customary rule for the selection,installation and maintenance of the electrical devices which may have explosive gas environment | |
| AS2293 Fire detection and alarm in buildings | |
| AS300 Fire-fighting equipment and elevators in the wire regulation | |
| GB/T16895.15-2002 Electrical devices in buildings-carrying capacity of the wiring system | |
| BS7671 Electrical installation requirements(England) | |
| 08ZD02 Standard design of electrical atlas of buildings in the mid—south region |
Design and Model Selection Method
BTTQ,BTTVQ and WD-BTTYQ(light-duty)apply to occasions where the voltage between wire core and sheath,between wire core and wire core is no larger than 500V alternating current and direct current virtual value.
Under following circumstances.mineral insulated cable shall be used with plastic sheath.
1.1If the cable is laid where it is corrosive to copper sheath:
1.2When the cable is buried directly or in conduits;
1.3When the cable is exposed in non-technical space of buildings,where have aesthetic
requirements; For fire prevention places.halogen-free low-smoke plastic outer sheaths shall be used.
2.1.1 According to different cable temperatures mineral insulated cable has 2kinds of current-carrying capacity.
Current-carrying capacity when the temperature is 70℃ .
Current-carrying capacity when the temperature is105℃ .
2.1.2 Under following laying conditions,current-carrying capacity shall be chosen according to normal operation temperature-70℃.
a. Exposed laying along walls,brackets,roof plates and bridges;
b.Mineral insulated cable is laid together with other types of cables in the same bridge,silo,cable trench and cable tunnel.
c.Other places where too high temperature of cable sheaths easily hurt humans or damage the equipment.
2.1.3 If mineral insulated cable is laid separately in bridges,cable trenches and conduits where no human touches it,current-carrying capacity can be chosen according to normal operation temperature 105℃.
2 . 2 According to actual length of line and length of delivered cable,we shall reasonably decide the specification of mineral insulated cable.
Because machining length of mineral insulated cable is constricted by raw materials, delivery length of large-size single core and multi-core cable is unable to as long as that of plastic cables. Therefore, please consider the delivery length of cable when choosing the specification,and avoid joints in the middle as much as possible.
Example 1: calculate a line whose load is 1000A, and maximum operation temperature doesn't exceed 70℃.As a result, 400 mm² is chosen according to Table 3. Delivery length is 60 meters according to “cable data sheet”: if the line is longer than 60 meters, please choose 240m²double combinations.Middle joints can be avoided if delivery length reaches 99 meters, and longer lines can uses 240m² double combinations. The longer the line is,the more complex the laying condition is. It is easy to lay small-size cables.
Example 2: Use 4×25mm² multi-core cable according to load calculation. If it is longer than delivery length 124 meter, consider using 4×(1X25) single-core cable,whose delivery length reaches 425 meters and middle joints are Unnecessary.
3.2 Corresponding to over 16mm² plastic cable,the section can be reduced. If plastic
cable is designed 4x185+95, the Corresponding mineral insulated cable is BTTZ 4X(1X150). 3.3 It is not necessary to consider coefficients in the case of double Combinations and multiple combinations.
3.4 If double combinations or multiple combinations of large-section cables are used to replace bus duct, construction investment can be reduced and line security is enhanced.
3.5 Our special branch terminal box makes cable branching possible (Refer to P28 for the Branch Box).
Product display
Application Fields
Mineral insulated cable has been widely used in high-rise buildings, shopping centers, star hotels, hospitals, theatre, conference centers libraries, museums, government offices, financial centers,TV and radio centers, sports centers, factories and mines, airports, tunnels,subways, light rails, underground garage, civil defense, boats, petrochemical, offshore oil platforms, aviation and aerospace, Steel metallurgy, tobacco and war industry and so on.
| Standard cross section of conductors mm² | Current carrying capacity A | ||
| Two loading conductors,two-core or single-core cables | Thee loading conductors | ||
| Multi-core cables or single-core cables lined up in a triangular shape | Single-core cables lined up in a flat array | ||
| 500V | |||
| 1.5 | 23 | 19 | 21 |
| 2.5 | 31 | 26 | 29 |
| 4 | 40 | 35 | 38 |
| 750V | |||
| 1.5 | 25 | 21 | 23 |
| 2.5 | 34 | 28 | 31 |
| 4 | 45 | 37 | 41 |
| 6 | 57 | 48 | 52 |
| 10 | 77 | 65 | 70 |
| 16 | 102 | 86 | 92 |
| 25 | 133 | 112 | 120 |
| 35 | 163 | 137 | 147 |
| 50 | 202 | 169 | 181 |
| 70 | 247 | 207 | 221 |
| 95 | 296 | 249 | 264 |
| 120 | 340 | 286 | 303 |
| 150 | 388 | 327 | 346 |
| 185 | 440 | 371 | 392 |
| 240 | 514 | 434 | 457 |
| 300 | 782 | 748 | 879 |
| 400 | 940 | 893 | 1032 |
Advantages of MI Cable