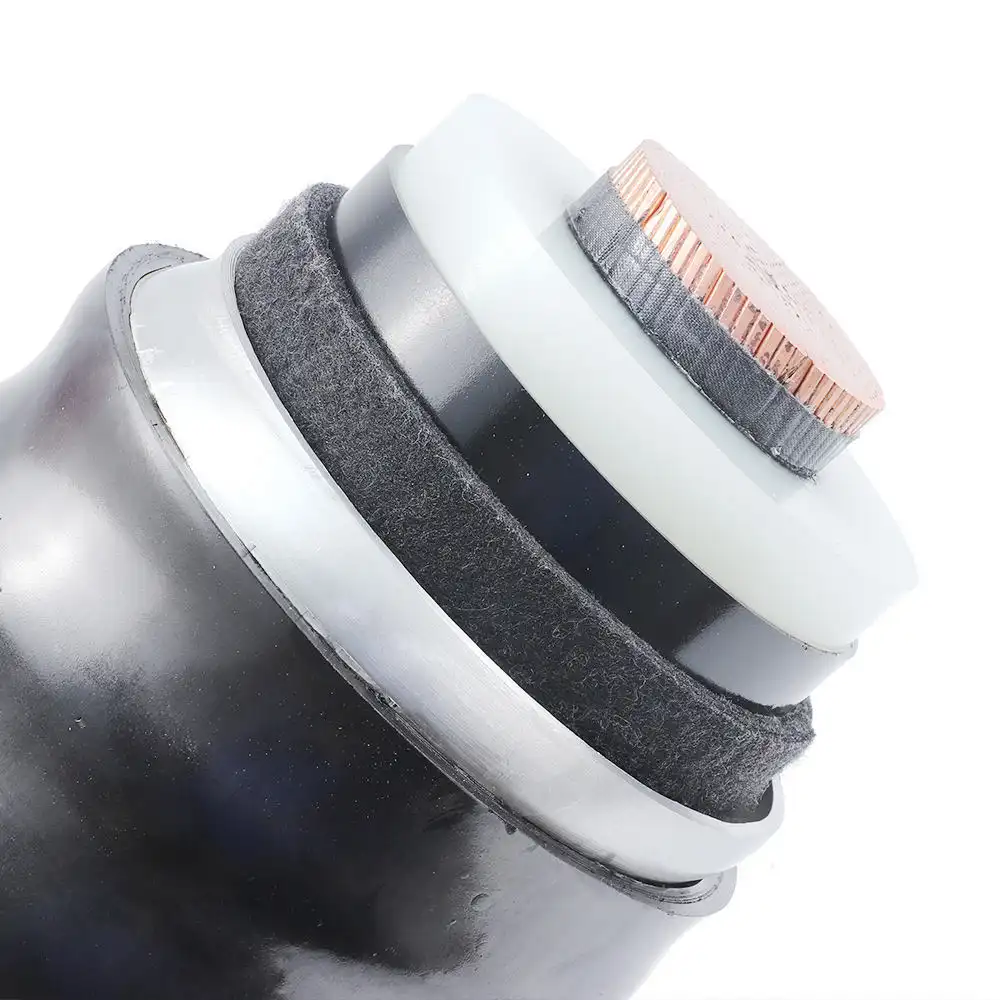
66-500kV XLPE POWER CABLE
Standard
● GB/T11017-2014 Power Cables with cross-linked polyethylene Insulation and their accessoried for Rated voltage of 110kV (Um=126kV)
● GB/T18890-2015 Power Cables with cross-linked polyethylene Insulation and their accessoried for Rated voltage of 220kV (Um=252kV)
● GB/T22078-2008 Power Cables with cross-linked polyethylene Insulation and their accessoried for Rated voltage of 500kV (Um=550kV)
UHV power cables: a strong pillar of power transmission
UHV power cables are the cornerstone of modern power transmission systems and play a key role in the energy sector thanks to their outstanding performance and unique characteristics.
Ultra-high voltage power cables are extremely delicate in design and manufacture, designed to cope with extremely high voltages and currents. These cables usually consist of a conductor, insulation, shield and sheath. The conductors are made of highly conductive materials, such as copper or aluminium, to ensure the efficient transmission of current. The insulation layer is made of advanced insulating materials, such as cross-linked polyethylene, to provide reliable electrical insulation and enable the cable to operate safely in ultra-high voltage environments. The shielding layer helps to reduce electromagnetic interference and ensure stable signal transmission. The sheath protects the internal structure of the cable from the external environment.
Ultra-high voltage power cables have excellent transmission capabilities. They are able to maintain low power losses over long distances, which is crucial for large-scale power transmission. By using UHV technology, electricity can be transmitted more efficiently across vast geographic areas, moving it from power plants to various points of demand in a continuous stream. This efficient transmission not only improves energy efficiency, but also reduces the impact on the environment.
In the operation of UHV power cables, their stability and reliability are crucial. They need to withstand a variety of environmental conditions, including high and low temperatures, humidity, and mechanical stress. To ensure their long-term stable operation, cable manufacturers conduct stringent quality inspections and performance tests to ensure that each cable has superior quality and performance. Meanwhile, in the process of cable installation and maintenance, professionals are also required to strictly follow the operating procedures to ensure the safe and reliable operation of the cable.
Ultra-high voltage power cables have a wide range of applications in the power system. They connect large power plants and high-voltage substations, building a huge power transmission network. In addition, they also play an important role in the transformation of urban power grids, industrial projects power supply and other fields. With the rapid development of the new energy industry, UHV power cables have also become an important link connecting new energy generation facilities and power grids, providing strong support for the grid connection and consumption of new energy.
|
Specification |
Name |
|
YJLW02 |
Power Cable with Copper Conductor, XLPE Insulation, Corrugated Aluminum Sheath, PVC Outer Sheath |
|
YJLW02—Z |
Longitudinal Water--blocking Power Cable with Copper conductor, XLPE Insulation, Corrugated Aluminum Sheath, PVC Outer Sheath |
|
YJLW03 |
Power Cable with Copper Conductor, XLPE Insulation, Corrugated Aluminum Sheath, PE Outer Sheath |
|
YJLW03—Z |
Longitudinal Water-blocking Power Cable with Copper Conductor, XLPE Insulation, Corrugated Aluminum Sheath, PE Outer Sheath |
|
YJLLW02 |
Power Cable with Aluminum Conductor, XLPE Insulation, Corrugated Aluminum Sheath, PVC Outer Sheath |
|
YJLLW02—Z |
Longitudinal Water-blocking Power Cable with Aluminum Conductor, XLPE Insulation, Corrugated Aluminum Sheath, PVC Outer Sheath |
|
YJLLW03 |
Power Cable with Aluminum Conductor, XLPE Insulation, Corrugated Aluminum Sheath, PE Outer Sheath |
|
YJLLW03—Z |
Longitudinal Water-blocking Power Cable with Aluminum Conductor, XLPE Insulation, Corrugated Aluminum Sheath, PE Outer Sheath |
Product description
PVC sheathed cables shall not be installed in the environment temperature is below and if it is below 0℃,the cable should be heated before the installation.
Cables with PE outer sheath(Type 03)are suitable for high voltage transmission line directly buried underground with higher insulation requirement on the outer sheath;and if they are laid in tunnels or vertical shafts,anti-fire and flame-retardant measures must be taken.
Fire resistance of cables in accordance with IEC 60331-21.
Fire non-propagation according to IEC 60332-3-22. LSHF (Low Smoke Halogen Free) according to IEC 60754-1.
Low smoke emission according to IEC 61034: light transmittance > 60%.
Low corrosive gases emission according to IEC 60754-2.
xlpe,pvc Power cable certificate display
Currant-carrying capacity and influencing factors
Currant-carrying capacity for cables with copper conductor,XLPE insulation under max.operating temperature (Unit:A)
|
Nominal cross sectional area |
Voltage level KV |
|||||||||||
|
66 |
110 |
220 |
||||||||||
|
Trefoil Laying |
Parallel Laying |
Trefoil Laying |
Parallel Laying |
Trefoil Laying |
Parallel Laying |
|||||||
|
In Air |
Buried |
In Air |
Buried |
In Air |
Buried |
In Air |
Buried |
In Air |
Buried |
In Air |
Buried |
|
|
240 |
625 |
545 |
650 |
570 |
615 |
535 |
650 |
555 |
- |
|
一 |
- |
|
300 |
715 |
615 |
750 |
645 |
710 |
605 |
745 |
635 |
|
|
|
|
|
400 |
820 |
695 |
865 |
735 |
810 |
685 |
860 |
720 |
805 |
670 |
850 |
680 |
|
500 |
950 |
790 |
1010 |
835 |
935 |
780 |
1000 |
825 |
920 |
750 |
958 |
775 |
|
630 |
1090 |
890 |
1170 |
950 |
1075 |
860 |
1155 |
935 |
965 |
850 |
1130 |
880 |
|
800 |
1330 |
1060 |
1435 |
1120 |
1295 |
1035 |
1395 |
1090 |
1280 |
985 |
1385 |
1010 |
|
1000 |
1515 |
1185 |
1640 |
1250 |
1470 |
1150 |
1585 |
1225 |
1455 |
1080 |
1560 |
1130 |
|
1200 |
1650 |
1275 |
1800 |
1360 |
1600 |
1235 |
1730 |
1320 |
1585 |
1140 |
1710 |
1215 |
|
1400 |
1780 |
1360 |
1955 |
1460 |
1735 |
1325 |
1890 |
1415 |
1730 |
1205 |
1880 |
1290 |
|
1600 |
1930 |
1445 |
2135 |
1560 |
1860 |
1405 |
2025 |
1505 |
1845 |
1260 |
2005 |
1350 |
|
2000 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2050 |
1310 |
2265 |
1450 |
|
2500 |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
- |
2305 |
1410 |
2530 |
1580 |