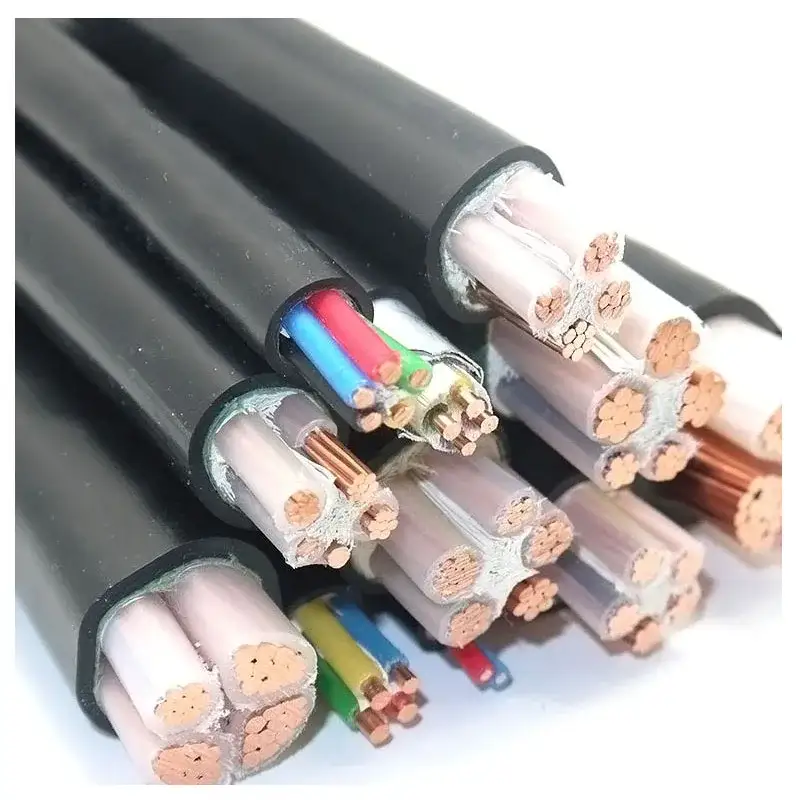
Aluminum Core Copper Core Cables Single-core Building Construction Vv Vy Vv62 Vv63 Vlv Vly Armoured Cables
5.0
Shipping:
Ocean freight
Place of Origin:
China
Payments:
L/C,D/A,D/P,T/T,Western Union,MoneyGram,OA
Lead Time:
1-1000(meters):15(days),>1000(meters):To be negotiated(days)
Customization:
Customized logo (Min. Order: 1000 sets),Customized packaging (Min. Order: 1000 sets),Graphic customization (Min. Order: 1000 sets)
Model Number:
VV VY VV62 VV63 VLV VLY VLV62 VLV63
Brand Name:
WUCAI
design customization
Please fill out the form below to request a quote or to request more information about us. Please be sure to upload customized requirement documents or pictures, and we will get back to you as soon as possible with a response. we're ready to start working on your new project, contact us now to get started.
Resistance
send us inquiry
Standard
IECA, BS, DIN
Certificate
TUV CE
Usage
D.C System
Rated voltage
0.6/1 KV
Armour
Armoured / Non-magnetic material armour
Core
Single Core
Insulation
PVC
Product name
PVC insulated single-core cables for rated voltage 0.6/1kV
Jacket
PE/PVC, PVC/PE
Conductor Material
Aluminum/Copper
Application
Underground, Construction
Type
LOW VOLTAGE
Insulation Material
PVC
Place of Origin
China
Products Description
The armoured single-core cables are used for D.C. system only.
As for A. C. system, non-magnetic armour material should be used, or magnetic isolation should be applied.
No. of cores:1
Conductor : Copper/Aluminum
Insulation: PVC
Jacket : PVC/PE
Rated Voltage: 0.6/1KV
Armoured : Armoured/Non-Armoured/non-magnetic steel tape(wire)
Product Paramenters
Type | No. of cores | Nominal Cross sectional area mm2 | ||
Coper conductor | Aluminum conductor | |||
VV VY VV62 VV63 | VLV VLY VLV62 VLV63 | 1 | 1.5~800 10~800 | |
Working temperature: | The long-term working temperature is not more than 70 °C, and the laying temperature is not lower than 0 °C; the allowable temperature of the cable conductor is 160 °C during short circuit (long-term duration is less than 5s). |
Allowable bending radius: | not less than 10 times the outer diameter of the cable |
Usages: | Generally used as a power transmission hub, often buried in the soil or laid indoors, in trenches, tunnels, with small insulation distance between lines, no poles and towers, small footprint, and basically no space on the ground. |
Common specifications and models: | the number of cores includes 2 cores, 3 cores, 4 cores, 5 cores, 3+1, 3+2, 4+1; |
The cross- sectional area (mm²) | The cross section includes from 1.5 mm2--240mm2, such as VV3*95+1*50 cable represents a cable composed of 3 strands of 95 square cores plus 1 strand of 50 square cores, other synonymous. |
Product Name | -- The full name of VV cable is copper (aluminum) core PVC insulated PVC sheathed power cable, which is an important member of power cables. The two letters V represent that the insulation and sheath materials are all PVC. |
VV & YJV | -- VV cable is a very common type of power cable, and its function is the same as that of YJV cable most of the time, although theoverall performance is not as good as that of YJV cable, and it is gradually replaced by YJV cable. |
Details Images
Company Profile
Wuxi Jiangnan Cable Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as “the Company”)a National Key High and New Tech Enterprise specialized in production, sales and research on cables & wires. It is a national customer satisfaction benchmark enterprise, "Top 500 China's Manufacturing Industry", "Top 500 China's Private Enterprises", "Top 500China's Machinery Industry", and "Top 500 China's Energy Groups", "China's Quality Integrity Enterprise". The "Wu Cai" brand was awarded the title of "Top 500 Asian Brands" and "Internationally Famous Brands Focused on Cultivation and Development in Jiangsu Province".
The company covers an area of more than 650,000 square meters, with a construction area of 400,000 square meters, and total assets of more than 8 billion Yuan. There are more than 2,200 employees, among them, junior and senior technical and managerial personnel account for more than 30% of the total number of employees.
The company is located in the national wire and cable industry base -- Guanlin Town, Yixing City, Jiangsu Province. It has always adhered to the business philosophy of "integrity and pragmatic, customer first" and is willing to supply more high quality products, perfect service, as always with new and old friends at home and abroad for sincere cooperation, mutual benefit and win-win!
Our Advantages
Certifications
Customer Photos
FAQ
1. who are we?
Wuxi Jiangnan Cable Co., Ltd. is a National Key High and New Tech Enterprise specialized in production, sales and research on cables & wires. It has enterprise the "Top 500 China's Manufacturing Industry", "Top 500 China's Private Enterprises", "Top 500China's Machinery Industry", and "Top 500 China's Energy Groups", "China's Quality Integrity Enterprise". The "Wu Cai" brand was awarded the title of "Top 500 Asian Brands". The company was listed in Hong Kong in April 2012, stock code: 01366.
2.what can you buy from us?
The company mainly produces products of more than 100 varieties and more than 40,000 specifications in three categories, including power cables up to 500kV, electrical equipment cables, and bare wires up to 1100kV.The company also produces flexible mineral insulated fireproof cables, photovoltaic cables, electric vehicle charging cables, locomotive cables, UHV supporting heat-resistant expanded conductors and other special cables.
3. how can we guarantee quality?
The company always regards quality and service as the foundation of the company's survival. It conducts strict inspections from raw materials entering the factory to finished products leaving the factory. The company adopts foreign advanced online polarization meters, high-voltage series resonance, partial discharge and other high-tech instruments to monitor the manufacturing process. The quality of the company is strictly controlled, so that the stability of the product can be reliably guaranteed.
4. why should you buy from us not from other suppliers?
The company currently has 1600 sets of advanced production and testing equipment, including V C V vertical and C C V catenary ultra-high voltage cross-linked cable production lines from Finland, the Coiling and frame twisting equipment from Germany and France, wire drawing production line from Italy and ultra-high voltage cable partial discharge detection system from Switzerland.
In addition, We have a national post-doctoral research workstation, technology center, laboratory and testing center. Our products have passed many international standard certifications, such as C E, S A B S, RoHS, C B, T U V.
5. what services can we provide?
Accepted Delivery Terms: FOB,CFR,CIF,EXW;
Accepted Payment Currency:USD,EUR,GBP,CNY;
Accepted Payment Type: T/T,L/C,Credit Card,PayPal;
Language Spoken:English,Chinese,Spanish,Japanese,Portuguese,German,Arabic,French,Russian,Korean,Hindi,Italian
{{item.score}} Stars
{{item.pre}}%
{{item.nickname ? (item.nickname.slice(0, 2) + '*****') : item.source === 1 ? 'mall buyer' : '--'}}
{{item.comment_time}}
Review in the {{item.country}}
{{itemAttr.params_key}}: {{itemAttr.params_value}}
Leave a message
Get in touch with us
Just leave your email or phone number in the contact form so we can send you a free quote for our wide range of designs! If you have any questions or needs, you can contact us immediately
Related Products
no data
We are a National Key High and New Tech Enterprise specialized in production, sales and research on wires and cables.
Contact person: Avery Yuan
Contact number: 86-17368469025
Email: avery@jncable.com.cn
WhatsApp: 86-17368469025
Contact person: Mandy Li
Contact number: 86-17368476738
Email: mandy@jncable.com.cn
WhatsApp: 86-17368476738
Copyright © 2025 Jiangnan Cable | Sitemap